Packaging Machines Glossary: Integrated Solutions for Marking and Coding on Industrial Packaging
Packaging represents an essential factor contributing decisively to the commercial success of virtually every product. Effective packaging impacts the entire production, distribution, sales, and consumption chain. In industrial contexts, efficient packaging relies heavily on centralized production facilities that emphasize manufacturing efficiency, storage optimization, streamlined distribution, clear identification, and precise traceability.
Decisions made regarding packaging can significantly influence production costs and the selection of manufacturing and distribution technologies. Effective packaging often shapes consumer perceptions and consumption patterns, thus demanding deep industry expertise to ensure optimal design and product preservation.
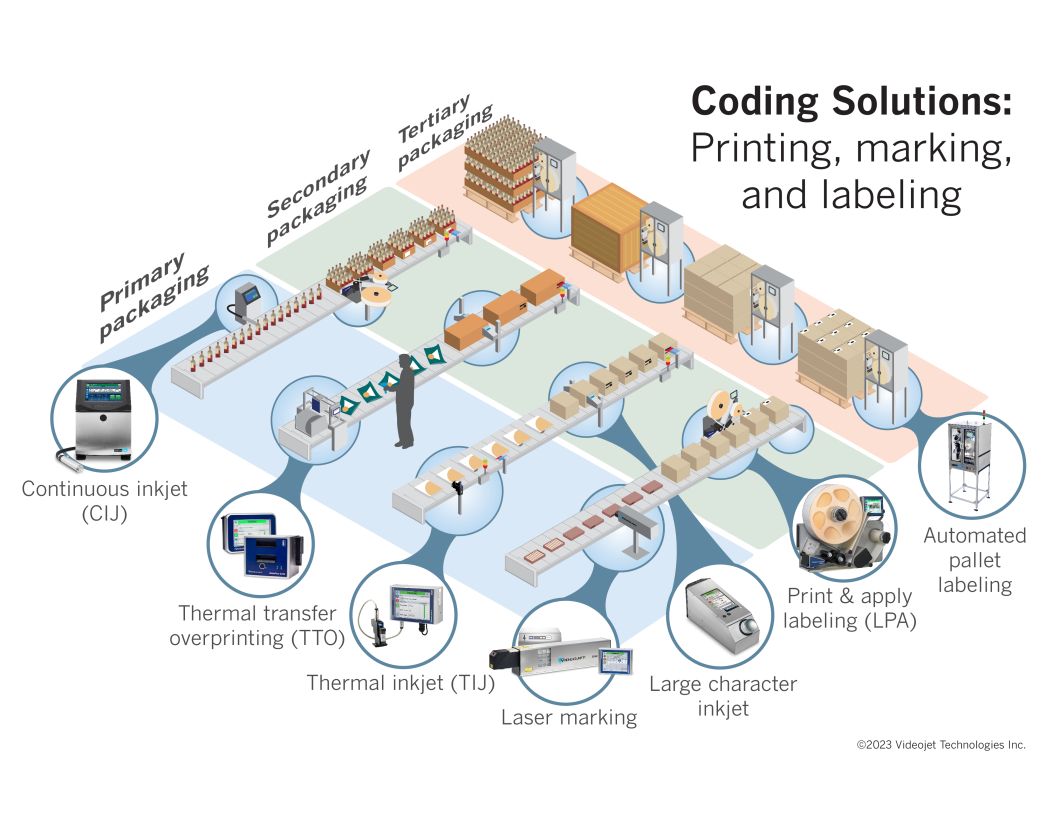
Primary Packaging
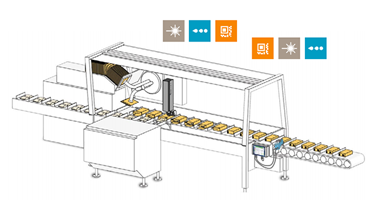
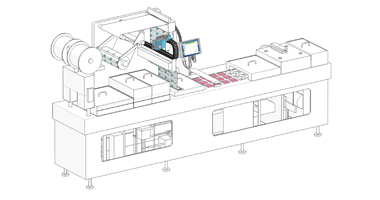
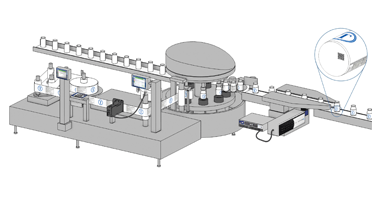
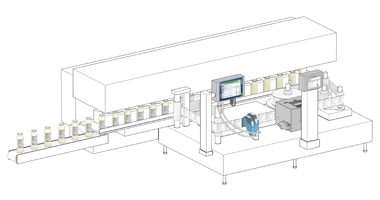
In the context of primary packaging, labeling can be applied directly onto the packaging surface or via printed paper or plastic labels affixed to the product. In addition to providing product details and brand information, primary packaging labels must incorporate clear coding that facilitates efficient product tracking and traceability. This is essential for enabling timely recalls of defective or contaminated items. Specifically, pharmaceutical products require unique identification codes to combat counterfeit medications effectively.
Secondary Packaging
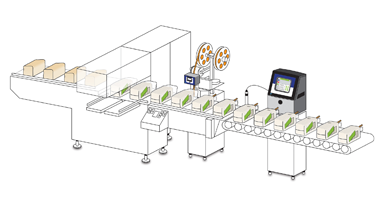
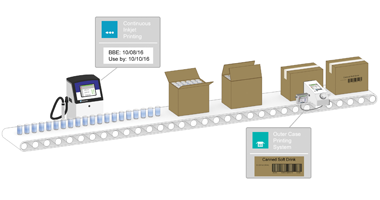
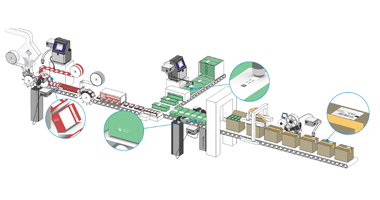
Labeling on secondary packaging serves to accurately identify contents within cartons, multi-package sleeves, or shipping cases, ensuring packages reach their intended destinations securely and efficiently. Secondary packaging comprises individual product cartons, multi-item sleeves, larger shipping cases, and stretch-wrapped palletized loads. Corrugated cases and shrink-wrapped films are commonly used for creating shipping units.
Each secondary packaging level must feature content identification in both human-readable form and machine-readable barcodes, including 1D and 2D codes. This requirement is particularly crucial for food products, as large retailers and supermarkets enforce strict standards, rejecting shipments that fail to meet these coding requirements. Such standards also extend to personal care products, pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and chemicals.
Industry Overview
The packaging industry consists of national companies and large multinational corporations capable of addressing diverse global market demands and setting international quality standards, technological innovations, functional requirements, and trends. These extensive packaging networks rely on a sophisticated ecosystem that includes:
- Providers of raw materials such as plastic resins, sheet metals, cellulose, and soda ash.
- Suppliers of essential inputs including adhesives, paints, colorants, and coatings.
- Ancillary product suppliers offering items like caps, seals, ribbons, as well as transport and logistics companies.
- Designers, consumer goods enterprises, technical and professional training providers, laboratory facilities, research and development (R&D) centers, and regulatory bodies.