Picture a world where every piece of packaging you encounter is designed not just for convenience, but with the planet in mind. A world where waste is minimized, recycling is maximized, and sustainability is at the forefront of every decision. This is the vision behind the European Union’s Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation (PPWR).

PPWR will require all members of the value chain to support the targets of this regulation. Videojet, a leader in the marking and coding industry, keeps a close eye on sustainability regulations and trends to assist brands and manufacturers in understanding the regulatory requirements. Also, by identifying and integrating the marking and coding solutions that are the best fit for an application, we help these brands and manufacturers achieve compliance.
What is the EU Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation?
The Packaging and Packaging Waste Regulation, more commonly known as PPWR, is a European Union-wide regulation promoting more sustainable packaging, both through design innovation and infrastructure, to transition to a circular economy. The European Council adopted the regulation in December 2024. It entered into force on February 11, 2025, with the provisions set to be generally applied starting August 12, 2026. As an evolution of the Packaging and Packaging Waste Directive 94/62/EC originating in 1994, the move from Directive to Regulation creates further harmonization in solving for sustainable packaging. Impacting packaging both manufactured in and imported into the EU, this regulation has global implications.
Stay ahead with real-time updates on the latest news:
The European Packaging Crisis: An alarming increase in CO2 emissions and ocean pollution
The excessive use of packaging, the proliferation of non-recyclable packaging, and the lack of clear recycling directions for consumers are just some of the contributing factors to the astounding impact that packaging waste is having in Europe:
- Packaging waste: According to the European Parliament, the EU realized an overall total increase in packaging waste, from 66 million tons in 2009 to 84 million tons in 2021. Each European generated an average of 188.7 kg in packaging waste in 2021.1
- CO2 emissions: An estimated 20-30 million tons of plastic waste is incinerated in Europe annually, leading to around 50-80 million tons of CO2 emissions each year, according to European Environment Agency.2
What are the goals of the PPWR?
The PPWR aims to reduce the overall environmental impact of packaging and guide the packaging industry towards a more circular, sustainable, and competitive economy. To do this, the PPWR mandates recyclability capabilities, limits harmful substances such as per/polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS), and standardizes labeling for better waste sorting and consumer clarity. Key goals include:
- Reducing packaging waste generation
- Promoting a cost-effective circular economy for packaging
- Increasing the use of recycled content in packaging

The PPWR sets mandatory reuse targets, limits single-use plastic packaging, and requires businesses to minimize packaging usage. Each EU country must reduce packaging waste per capita compared to 2018 levels: at least 5% by 2030, 10% by 2035, and 15% by 2040.4 Additionally, recycling targets are set for packaging waste overall and by waste types:
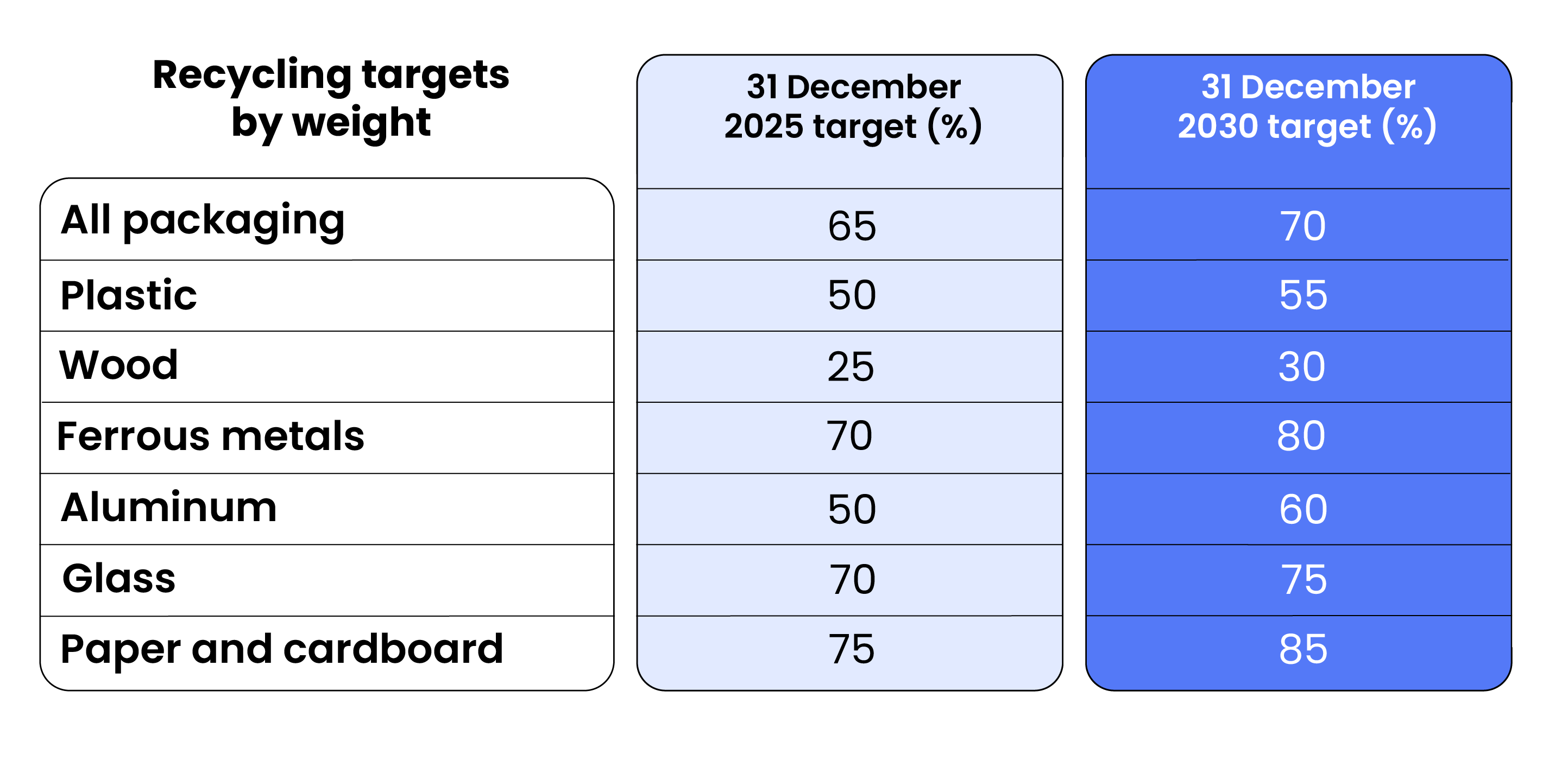
PPWR recyclability targets: Strict performance grades
PPWR introduces three recyclability performance grades with stricter requirements through 2038. By 2030, packaging that is less than 70% recyclability by weight (Grade C) will be defined as technically non-recyclable. By 2038, Grade C packaging will no longer be acceptable on the market. Packaging that includes multiple materials that are challenging to recycle, for example, are at risk of non-compliance. Further information on recyclability is expected in a delegated Act. In general, there are some key performance grades and recyclability factors to consider:
- Separability of packaging components
- Efficiency of sorting and recycling processes
- Advancements in sorting and recycling technologies
- Preservation of secondary raw materials’ functionality
Stay tuned for Part 2 of our PPWR article which will cover key topics like Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR), recycled content requirements for plastic packaging, and other important regulations. Learn how PPWR aims to increase packaging reuse, minimize harmful substances, support reuse/refill systems, and recommend QR® codes5 for consumer education. Stay informed about the implications for packaging producers and how to prepare for the new recyclability requirements.
Sources:
2 https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/plastics-the-circular-economy-and page 44
3 https://www.eea.europa.eu/en/topics/in-depth/plastics?activeTab=fa515f0c-9ab0-493c-b4cd-58a32dfaae0a
5 QR Code is a registered trademark of DENSO WAVE INCORPORATED.
